On January 15th, 2025, the Japanese commercial space company ispace launched its HAKUTO-R Mission 2 Resilience to the Moon. On June 5th, 2025, the lander crashed down on the lunar surface due to a malfunction with its Laser Range Finder (LRF). Six days later, NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) captured photos of the site where RESILIENCE experienced a hard landing.
The image, shown above, was acquired by LRO's right Narrow Angle Camera while the orbiter was at an altitude of about 80 km (50 mi) above the Mare Frigoris region (Latin for "Sea of Cold"). This region in the Moon's northern hemisphere is characterized by volcanic soil interspersed with large-scale faults (aka wrinkle ridges). The landing site is visible as a dark smudge (just above the arrow), which was created when the lander crashed down, kicking up subsurface regolith in the process. It is surrounded by a bright halo, the result of surface regolith scattered by the impact and scoured the surface.
Despite the loss of Resilience and its predecessor, HAKUTO-R Mission 1, ispace is committed to conducting lunar exploration using its commercial landers, rovers, and other robotic elements. Earlier today, the company released its Technical Cause Analysis for the HAKUTO-R Mission 2 crash, which confirmed that an anomaly with the lander's LRF was responsible.
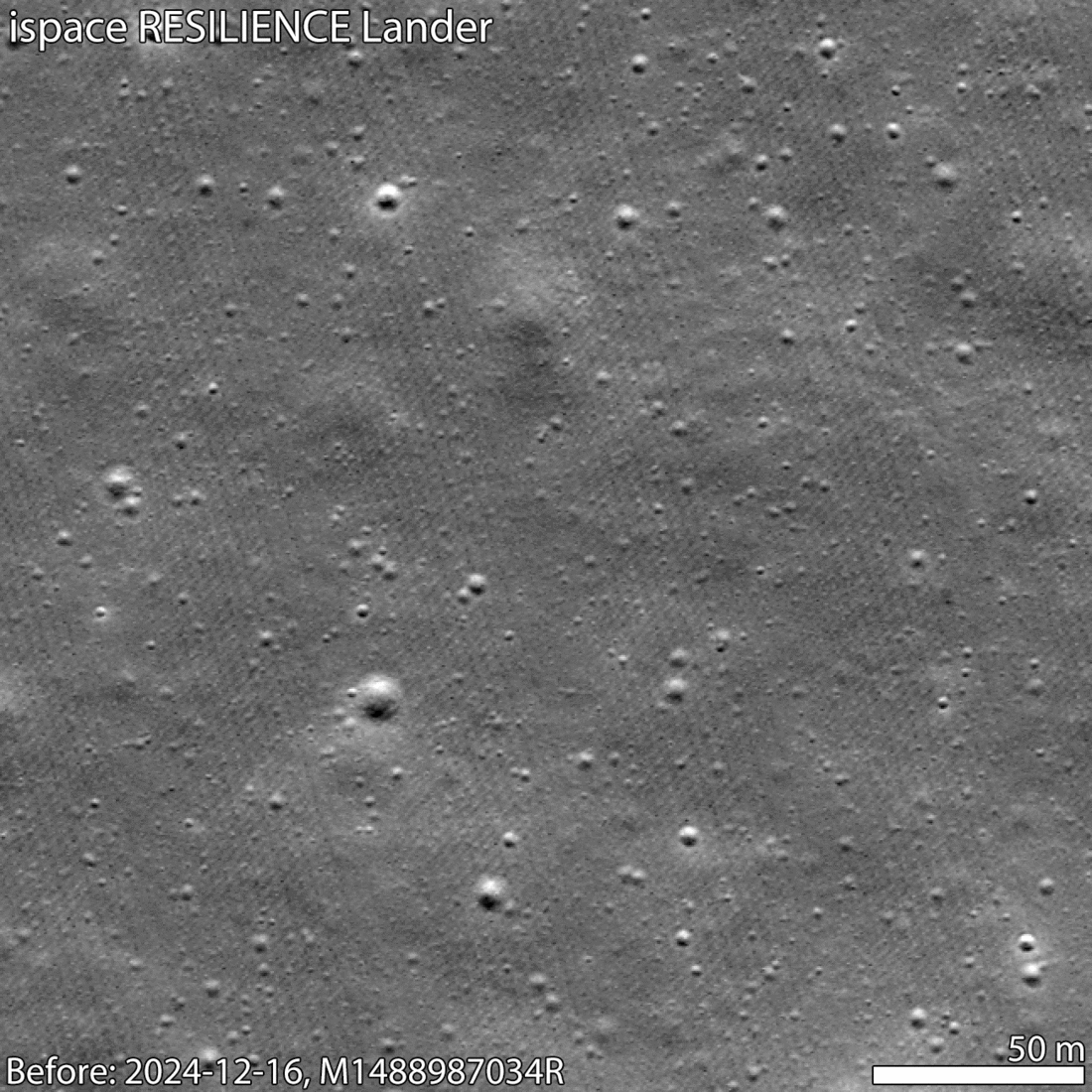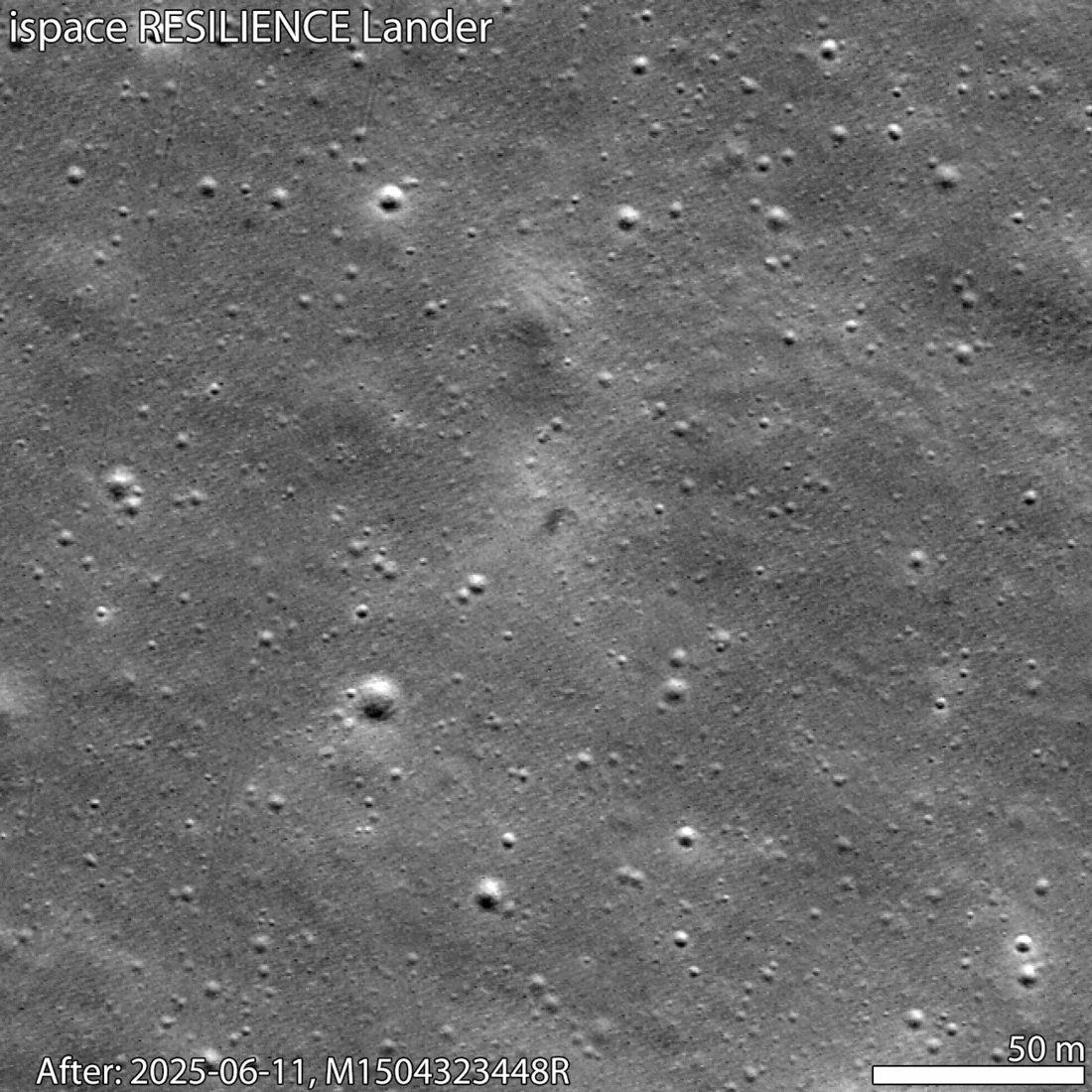 Temporal sequence showing site before and after impact. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University
Temporal sequence showing site before and after impact. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University
Further Reading: NASA

